
| COULEUR | Feuillage tricolore |
|---|---|
| CYCLE DE VIE | Succulent |
| ESPACEMENT | 10-15 cm (4-6″) |
| EXPOSITION | Soleil |
| HAUTEUR | 10-15- cm (4-6″) |
| PORT | Arrondi |
| SOL | Bien drainé |
| TAILLE DU POT | 3.5″ – 9 cm couleur |
| TYPE DE PLANTE | Plante à feuillage |
| GENRE | Sedum |

Benoit Geneslay Conseil

| COULEUR | Feuillage tricolore |
|---|---|
| CYCLE DE VIE | Succulent |
| ESPACEMENT | 10-15 cm (4-6″) |
| EXPOSITION | Soleil |
| HAUTEUR | 10-15- cm (4-6″) |
| PORT | Arrondi |
| SOL | Bien drainé |
| TAILLE DU POT | 3.5″ – 9 cm couleur |
| TYPE DE PLANTE | Plante à feuillage |
| GENRE | Sedum |
La plante de porcelaine.
Appelée aussi ‘Plante de porcelaine’ car ses feuilles se détachent facilement dès qu’on l’effleure. Cette plante est d’une grande robustesse et très prolifique, chaque feuille tombée, par bouturage, donne une nouvelle plantule. Feuillage de couleur bleue pale ou rose pale selon les conditions de culture

Dénomination
Maintenant, si vous avez fait l’impensable et supprimé quelque chose dont vous aviez vraiment besoin dans la Corbeille, voici comment le récupérer dans Time Machine (si le stockage est un autre disque dur, vous devrez d’abord le connecter à votre Mac) :
Ouvrez au hasard des pages de journaux, de revues, de sites d’information ou de réseaux sociaux, et relevez tous les nombres que vous y trouvez. Puis intéressez-vous au premier chiffre significatif de chacun de ces nombres : c’est le chiffre le plus à gauche, qui n’est pas zéro. Ne tenez compte ni du signe ni de la place de la virgule : par exemple, le premier chiffre significatif des nombres 0,038 3,14159 et -32 est 3. On peut penser a priori que chacun des chiffres de 1 à 9 sera vu avec la même fréquence comme premier chiffre significatif. Pourtant, si vous relevez beaucoup de nombres d’origines variées, vous constaterez que le chiffre 1 apparaît au début de près d’un tiers des nombres, le chiffre 2 environ une fois sur 6, et que les fréquences diminuent jusqu’au chiffre 9 (moins d’une fois sur 20).
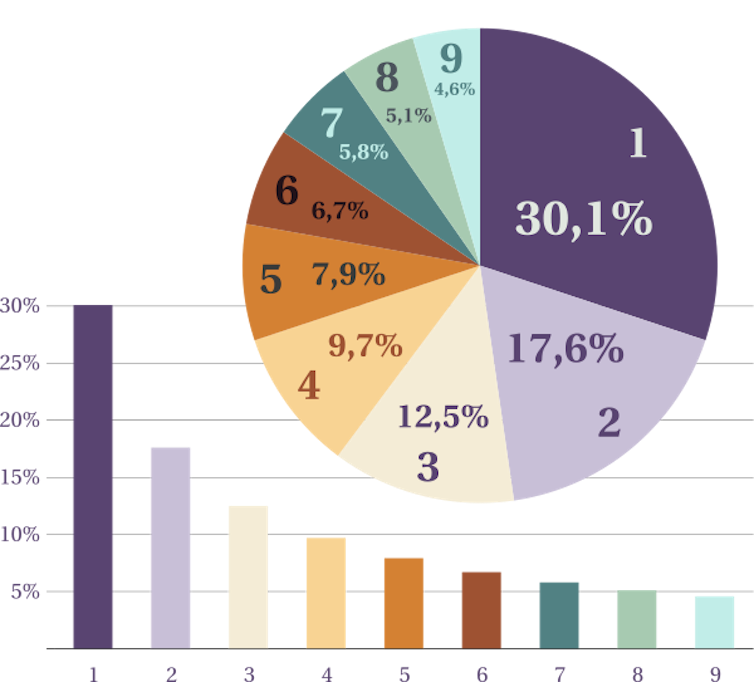
Cette distribution du premier chiffre significatif est aujourd’hui connue sous le nom de « Loi de Benford », d’après l’ingénieur américain qui l’a vérifiée en 1938, en répertoriant plus de 20 000 nombres provenant de multiples sources (longueurs de fleuves, cours de la bourse, résultats de base-ball, poids des éléments chimiques, etc.).
Frank Benford propose même une formule précise pour décrire avec quelle distribution apparaissent les chiffres de 1 à 9 comme premier chiffre significatif : la fréquence du chiffre i (i variant entre 1 et 9) est donnée par le logarithme à base 10 de (1+i)/i. Par exemple lorsque i est le chiffre 2, vous pouvez vérifier sur une calculatrice que la fréquence donnée par la formule de Benford vaut :
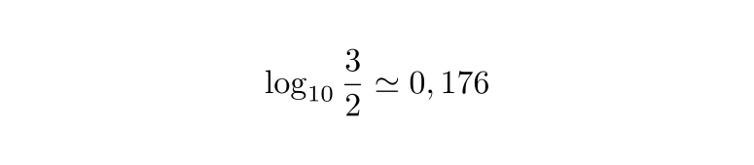
La fonction logarithme qui apparaît dans la formule ci-dessus a joué un grand rôle dans la découverte de cette étrange loi. Le logarithme était très utilisé avant l’avènement de l’ordinateur pour sa faculté à transformer les multiplications et divisions, opérations très compliquées à effectuer à la main, en additions et soustractions (un peu plus simples !). Pour effectuer des calculs, on avait donc couramment recours à des tables de logarithmes, petits livres qui donnaient les logarithmes des nombres que l’on voulait multiplier.
Ainsi, pour calculer rapidement le quotient 12 345 ÷ 6 789, on commençait par consulter la table pour obtenir les logarithmes de 12 345 et 6 789, qui valent respectivement 4,0915 et 3,8318. On calculait à la main la différence entre ces deux nombres, qui donne 0,2597, puis en utilisant dans l’autre sens la table de logarithmes, on trouvait le quotient, qui est le nombre dont le logarithme est égal à cette différence, soit environ 1,818.

C’est l’astronome américain Simon Newcomb qui a remarqué que les premières pages de ces tables de logarithmes étaient plus rapidement usées que les dernières, pour la raison que l’on utilisait plus souvent des nombres commençant par un 1 que par un 9. Newcomb publia le premier article sur cette surprenante distribution des premiers chiffres dès 1881, mais son travail est à l’époque passé inaperçu.
Près de 50 ans plus tard, en observant à nouveau l’usure irrégulière des tables de logarithmes, Benford refit la même découverte.
La distribution prédite par la loi de Benford se vérifie expérimentalement sur toute série de données issues du monde réel, pourvu que cette série soit assez « riche » (nombres d’origines variées et/ou réparties sur plusieurs ordres de grandeur).
En effet on comprend bien que, si par exemple on ne considère que des tailles d’individus exprimées en centimètres, le premier chiffre significatif sera presque tout le temps le 1 et donc la loi de Benford ne sera pas satisfaite. En revanche, la série constituée des nombres d’habitants par commune sur un territoire assez grand se conforme plutôt bien à la loi de Benford, car la taille des villes peut varier de quelques centaines à plusieurs millions d’habitants.
Ainsi, le graphique ci-dessous illustre les résultats obtenus en étudiant le premier chiffre significatif des nombres d’habitants des communes de la région Normandie. Globalement, on retrouve bien l’allure du diagramme en barres prévu par la loi de Benford.
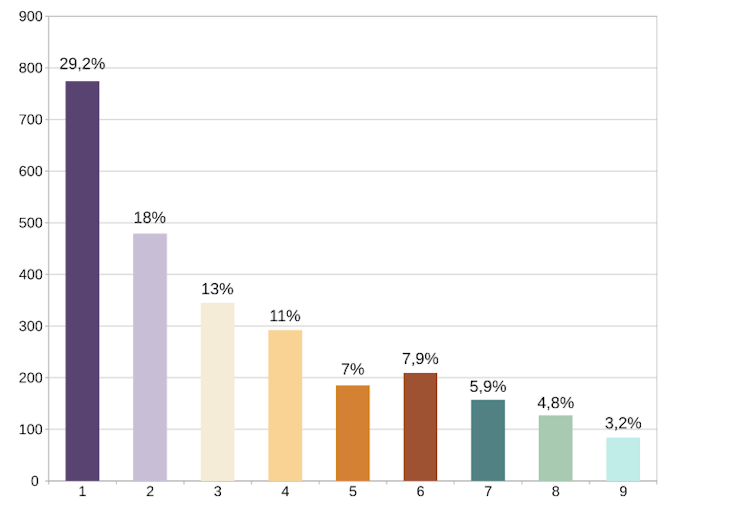
On peut se demander pourquoi le 1 et le 2 sont plus souvent utilisés comme premier chiffre significatif que le 8 ou le 9. Après tout, il y a autant de nombres dans l’intervalle [9 000, 10 000) (donnant un 9 comme premier chiffre) que dans l’intervalle [1 000, 2 000), qui vont donner un 1.
Mais l’erreur bien naturelle que l’on commet en comparant ainsi les tailles de ces deux intervalles consiste à les mesurer de manière additive : dans les deux cas, il faut ajouter 1 000 à la borne inférieure pour obtenir la borne supérieure. Or, comme le montre très bien Mickaël Launay dans son livre ce raisonnement « additif » n’est pas pertinent : quand on compare des nombres de la vie réelle, on le fait plutôt multiplicativement. La taille « multiplicative » du premier intervalle vaut 10 000 ÷ 9 000 soit environ 1,11, elle est beaucoup plus petite que celle du second, qui vaut 2 000 ÷ 1 000, soit 2.
Voici une situation très concrète pour montrer en quoi ce point de vue multiplicatif est beaucoup mieux adapté. Intéressons-nous aux prix de biens de consommation courante, et disons pour simplifier que ces prix suivent tous une même inflation lente et régulière. Prenons un prix dont le premier chiffre significatif est 1, disons la baguette de pain à 1 euro. Son premier chiffre significatif va rester 1 tant que le prix de la baguette n’aura pas atteint 2 euros, soit pendant tout le temps nécessaire pour obtenir une augmentation des prix de 100 %. Considérons en parallèle le prix d’un litre d’huile d’olive à 9 euros : son premier chiffre significatif restera 9 seulement le temps que l’inflation le fasse monter à 10 euros (augmentation de seulement 11 %).
En pensant ainsi multiplicativement, la distribution prédite par la loi de Benford devient beaucoup plus naturelle. Les intervalles [1,2), [2,4), [3,6), [4,8) et [5,10) ont la même taille multiplicative 2. Les sommes des fréquences des premiers chiffres significatifs vus dans chacun de ces intervalles sont alors égales :

Cette vision multiplicative se retrouve dans un autre argument couramment avancé pour expliquer la loi de Benford : la distribution du premier chiffre significatif doit être la même en France, où l’on mesure les distances en kilomètres et les prix en euros, qu’aux États-Unis où l’on utilise les miles et les dollars. Autrement dit elle ne doit pas dépendre du choix des unités utilisées pour mesurer les grandeurs. Ainsi les fréquences des premiers chiffres significatifs ne doivent pas changer si l’on multiplie toutes les données par un même nombre (ce qui correspond à un changement d’unité). Or la loi de Benford est la seule distribution qui satisfait cette invariance.
La loi de Benford peut sembler n’être qu’une curiosité anecdotique. Cependant, au début des années 90, l’économiste Mark Nigrini lui trouva une application très concrète : il eut l’idée de l’utiliser pour la détection de fraudes dans des données, et y a même consacré un ouvrage en 2012.
En effet, si une série de nombres variés provenant de données réelles suit théoriquement la distribution prédite par Benford, Nigrini montre que dans des données comptables falsifiées, la fréquence de nombres commençant par 5 ou 6 est largement plus élevée : la plupart des faussaires ignorent la loi de Benford ! Des experts-comptables peuvent ainsi mettre en évidence les fraudes des sociétés. Il semble courant aujourd’hui de se baser sur la loi de Benford (incluant des tests plus approfondis considérant également le second chiffre significatif des nombres) pour suspecter une fraude dans des données, qu’elles soient fiscales, comptables, électorales ou même scientifiques. Bien qu’un écart à la loi de Benford ne constitue pas une preuve de fraude, il peut orienter les experts vers des vérifications plus poussées.
| Chiffre | Fréquence |
| 1 | 30,10 % |
| 2 | 17,61 % |
| 3 | 12,49 % |
| 4 | 9,69 % |
| 5 | 7,92 % |
| 6 | 6,69 % |
| 7 | 5,80 % |
| 8 | 5,12 % |
| 9 | 4,58 % |
Event Log Message Descriptions for M580 CPUs (Firmware earlier than Version 4.0), BMENUA0100 and BMENOR2200H (Firmware earlier than Version 3.01)
This topic presents event log message descriptions for:
M580 CPUs with firmware earlier than version 4.0 (abbreviated “CPU” in column Devices), and
BMENUA0100 OPC UA communication modules (abbreviated “NUA” in column Devices), and
BMENOR2200H remote terminal unit (abbreviated “eNOR” in column Devices)
| Event Description | Event additional Description | Facility | Severity | MSGID | MSG:peerAddr | MSG:type | MSG:appMsg | Devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Successful connection to or from a tool or a device: * Successful login * Successful TCP connection |
Successful login (Data Storage via FTP, FDR Server via FTP, Firmware upload via FTP) |
10 |
6 |
FTP |
remote ip address |
Li1: Successful connection(MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_CNCTN_SUCCESS) |
« Successful login » |
CPU |
|
Successful login (Web Server via HTTPS) |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
« Successful login » |
NUA |
||||
|
Successful login (firmware upgrade via HTTPS) |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
« Successful login » |
NUA |
||||
|
Successful login (OPC-UA) |
OPC-UA |
« (null) » |
« Successful login » |
NUA |
||||
|
Successful login (Unity Application password via Modbus-Umas) |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« (null) » |
« Successful login » |
CPU |
||||
|
Successful login (Web Server via HTTP) |
HTTP |
« (null) » |
« Successful login » OR « Successful connection » (if no User Login M580 Web pages) |
CPU |
||||
|
Successful TCP connection (no user) |
MODBUS |
remote ip address |
« Successful connection » |
CPU |
||||
|
Successful TCP connection (no user) |
EIP |
« (null) » |
« Successful connection » |
CPU |
||||
|
Successful connection on DNP3 communication protocol (about DNP3 master and outstation) |
DNP3 |
remote ip address |
« Successful connection » |
eNOR |
||||
|
Successful connection on IEC60870 communication protocol (about IEC60870 client and server) |
IEC60870 |
remote ip address |
« Successful connection » |
eNOR |
||||
|
Connection problem to or from a tool or a device: *TCP connection problem due to ACL check (source IP address/TCP port filtering) * Login problem |
Login problem ( Data Storage via FTP, FDR Server via FTP, Firmware upload via FTP) |
10 |
4 |
FTP |
remote ip address |
Li2: Unsuccessful connection (wrong credential)(MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_CNCTN_FAILURE) |
« Failed login » |
CPU |
|
Login problem (Web Server via HTTPS) |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
« Failed login » |
NUA |
||||
|
Login problem (firmware upgrade via HTTPS) |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
« Failed login » |
NUA |
||||
|
Login problem (OPC-UA) |
OPC-UA |
« (null) » |
« Failed login » |
NUA |
||||
|
Login problem (Web Server via HTTP) |
HTTP |
remote ip address |
« Failed login » OR « Failed connection » (if no User Login) |
CPU |
||||
|
Login problem (Unity Application password via Modbus-Umas) |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
remote ip address |
« Failed login » |
CPU |
||||
|
TCP connection problem (no user) |
MODBUS |
remote ip address |
« Failed connection » |
CPU |
||||
|
TCP connection problem (no user) |
EIP |
remote ip address |
« Failed connection » |
CPU |
||||
|
Connection problem on DNP3 communication protocol (about DNP3 master and outstation) |
DNP3 |
remote ip address |
« Failed connection » |
eNOR |
||||
|
Connection problem on IEC60870 communication protocol (about IEC60870 client and server) |
IEC60870 |
remote ip address |
« Failed connection » |
eNOR |
||||
|
Disconnection triggered by local or peer: * TCP disconnection * On demand logout |
disconnection triggered by either the peer/user/local |
10 |
6 |
FTP |
« (null) » |
Li5: disconnection triggered by the peer/user(MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_DISCONNECTION) |
« Disconnection » |
— |
|
disconnection triggered by either the peer/user/local |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
« Disconnection » |
NUA |
||||
|
disconnection triggered by either the peer/user/local |
OPC-UA |
« (null) » |
« Disconnection » |
NUA |
||||
|
disconnection triggered by either the peer/user/local |
MODBUS |
remote ip address |
« Disconnection » |
CPU |
||||
|
— |
DNP3 |
« (null) » or remote ip address |
« Disconnection » |
eNOR |
||||
|
— |
IEC60870 |
« (null) » or remote ip address |
« Disconnection » |
eNOR |
||||
|
Automatic logout (inactivity timeOut) HTTPS OPC-UA |
Disconnection triggered by a timeout |
10 |
6 |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
Li6: Disconnection triggered by a timeout(MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_DSCNCT_TIMEOUT) |
« Auto logout » |
NUA |
|
Disconnection triggered by a timeout |
OPC-UA |
« Auto logout » |
NUA |
|||||
|
Major Changes in the system: Parameters run time change outside configuration |
Major change of cycle time or watch dog PLC application parameters change (cycle time, watch dog) |
13 |
5 |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« (null) » |
Li87: System parameter update (MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_PARAMETER_UPDATE) |
« XXXX parameter update » (with XXXX that identifies the parameter)XXXX = « Cycle time » Example: Cycle time parameter update |
CPU |
|
Major Changes in the system: * Application or Configuration download from the device * Export (recording) cybersecurity configuration files from the device |
Download of a configuration file from the device |
13 |
6 |
MODBUS |
« (null) » |
Li8: Download of a configuration file from the device(MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_CONF_DL) |
« Application download » or « Configuration download » |
CPU |
|
HTTPS |
« Cybersecurity configuration backup » |
NUA |
||||||
|
Major Changes in the system |
Upload of Application/Configuration or Configuration only into the device (including CCOTF) Import (restore) cybersecurity configuration file into the device |
13 |
6 |
MODBUS |
« (null) » |
Li9: Upload of a configuration file into the device(MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_CONF_UL) |
« Application upload » or » Configuration upload » |
CPU NUA |
|
HTTPS |
« Cybersecurity configuration restore » |
NUA |
||||||
|
Major Changes in the system |
Upload of Web pages into the device |
13 |
6 |
FTP |
« (null) » |
Li10: Upload of a new firmware in the device(MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_FIRMWARE_UPDATE) |
« Web pages upload » |
CPU |
|
Upload of new safety copro |
FTP |
« Safety copro firmware upload » |
CPU |
|||||
|
Upload of a new firmware in the device |
FTP |
« Firmware upload » |
CPU |
|||||
|
Upload of a new firmware in the device |
HTTPS |
« Firmware upload » |
NUA |
|||||
|
Major Changes in the system |
Modification of the time of the device |
13 |
6 |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« (null) » |
LI15: Modification of the time of the IED |
« Time major update » |
NUA |
|
Communication parameters run time Successful change outside configuration |
Enable/disable of communication services |
10 |
4 |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« (null) » |
Li18: Any port, either physical (Serial, USB) or logical (telnet, FTP) activation/deactivation (MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_PORT_MANAGEMENT) |
« Major communication parameter update: XXXX YYYY »XXXX = « EIP » or « DHCP » or « FTP » or « MODBUS » or « SNMP » or « HTTP » or « SECURITY » or « NTP » or « IPSEC » or « DEVICE_MANAGER » For NUA only:XXXX = « Control Expert Data Flows to CPU only » or « Control Expert Data Flows to Device Network » or « CPU to CPU Data Flows » For NOR only:XXXX = « DNP3 over TLS channel[« channel name »] » or « IEC60870 over TLS »YYYY= « enable » or « disable »Example: »Major communication parameter update: FTP enable » |
CPU NUA eNOR |
|
network physical port change: port link up/down |
Any network physical port status change. Can be the simple status of a Ethernet port, or information gathered from RSTP / HSR / PRP algorithm for redundant systems |
10 |
4 |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« (null) » |
LI19: Any network physical port status change. Can be the simple status of a Ethernet port, or information gathered from RSTP / HSR / PRP algorithm for redundant systems (MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_NETWK_PORT_CHG) |
« Major network physical port status change: XXXX link YYYY » XXXX = « ETH » following by decimal number for the port or « FRONT port » YYYY = « link up » or « link down » Example: « Major network physical port status change: ETH1 link up) |
CPU NUA |
|
Any topology change detected: |
Any topology change detected from RSTP / HSR / PRP |
10 |
4 |
RSTP |
« (null) » |
LI20: Any topology change detected from RSTP / HSR / PRP algorithms for redundant systems (MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_NTWK_TPLGY_CHG) |
« Topology change detected » or « Topology change detected: XXXX YYYY » XXXX = « ETH » following by decimal number for the port or « FRONT port » YYYY = « enable », « disable », « learning », « forward », « blocking » |
CPU NUA |
|
Integrity check error: * Digital Signature error, * Integrity only (hash mac) |
Firmware integrity error |
10 |
6 |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« (null) » |
LI84: Data Integrity Error MNT_ENG_MSG_DATA_INTEGRITY_ERROR |
« Firmware integrity error » |
CPU NUA |
|
Data integrity error: CS Conf, cert, whitelist, or RBAC) |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« Data integrity error » |
NUA |
|||||
|
Major Changes in the system: Reboot |
Reboot after firmware upload |
13 |
4 |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« (null) » |
LI14: MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_REBOOT_ORDER |
« Restart » |
CPU NUA |
|
Major Changes in the system |
PLC Operating Mode change (Run, Stop, Init, halt) Maintenance Mode Safety Operating Modes change (SafeRun, Stop Safe task) |
13 |
5 |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« (null) » |
LI85: Operating mode change MNT_ENG_MSG_OPERATING_MODE_CHANGE |
« XXXX state update: YYYY » (with XXXX that identifies the object which state change and YYYY that identifies the new state ) XXXX = « PLC » or « PLC safe task » or « Device » YYYY = « INIT » or « STOP » or « RUN » or « HALT » or « Maintenance mode » or « Safe mode » EXAMPLES: « PLC state update: RUN » « PLC state update: Maintenance mode » |
CPU |
|
Major Changes in the system: Hardware change |
operation on SDCard for module that have |
13 |
6 |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« (null) » |
LI26: Hardware change MNT_ENG_MSG_HARDWARE_CHANGE |
« Hardware update: XXXX » (with XXXX that describes the update) XXXX = « SD card insertion » or « SD card extraction » |
CPU |
|
Rotary Wheel position change: Reset, Advanced |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« Hardware update: XXXX » (with XXXX that describes the update) XXXX = « back to factory mode » or « secure mode » |
NUA |
|||||
|
Major change in Cybersecurity RBAC (done through Cybersecurity configuration web pages). |
Create user account Delete user account Update user account |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
Li11: MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_RBAC_UPDATE |
« Update RBAC » |
NUA |
||
|
Major change in Cybersecurity Policy (done through Cybersecurity configuration web pages). |
Network services Event log Security policy Security banner |
10 |
4 |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
Li12:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_SECURITY_UPDATE_UPDATE |
« Major Cyber Security parameter update: network services » « Major Cyber Security parameter update: event log » « Major Cyber Security parameter update: security policy » « Major Cyber Security parameter update: security banner » |
NUA |
|
Major change in Cybersecurity device specific parameters (done through Cybersecurity configuration web pages). |
Enable/Disable & configure IPSEC Enable/Disable & configure OPC-UA Enable/Disable & configure DNP3 |
10 |
4 |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
Li13: MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_DSS_UPDATE |
« Major Cyber Security parameter update: IPSEC » « Major Cyber Security parameter update: OPC-UA » |
NUA |
|
Authorization problem |
An action on a resource from a user or machine is not authorized |
10 |
4 |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
Li21: MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_AUTH_REQ |
« Failed authorization » |
— |
|
Certificate Management |
Add/remove Client certificate |
10 |
4 |
HTTPS |
« (null) » |
Li89: Certificate Management (MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_CERT_MGT) |
« Add client certificate » « Remove client certificate » |
NUA |
|
Certificate Management: * Certificate expired |
server certificate expiration detection on restart |
10 |
3 |
DEVICE_MANAGER |
« (null) » |
Li29: Certificate Management (MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_CERT_EXPIRE) |
« Certificate expired » |
NUA |
|
Specific for eNOR project: |
||||||||
|
Authentication problem |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li100:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_AUTHENTICATION_FAILUE |
« channel[« channel name« ] authentication failed » |
eNOR |
|
unexpected response |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li101:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_UNEXPECTED_RESPONSE |
« channel[« channel name« ] unexpected response » |
eNOR |
|
No response |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li102:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_NO_RESPONSE |
« channel[« channel name« ] no response » |
eNOR |
|
Aggressive mode not supported |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li103:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_AGGRESSIVE_MODE_NOT_SUPPORTED |
« channel[« channel name« ] aggressive mode not supported » |
eNOR |
|
MAC algorithm not supported |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li104:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_MAC_ALGORITHM_NOT_SUPPORTED |
« channel[« channel name« ] MAC algorithm not supported » |
eNOR |
|
Key wrap algorithm not supported |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li105:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_KEYWRAP_ALGORITHM_NOT_SUPPORTED |
« channel[« channel name« ] key wrap algorithm not supported » |
eNOR |
|
Authorization problem |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li86:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYP_AUTHORIZATION_FAILURE) |
« channel[« channel name« ] authorization failed » |
eNOR |
|
Update key change method not permitted |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li106:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_UPDATE_KEY_CHANGE_METHOD_NOT_PERMITTED |
« channel[« channel name« ] update key change method not permitted » |
eNOR |
|
Invalid signature |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li107:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_INVALID_SIGNATURE |
« channel[« channel name« ] invalid signature » |
eNOR |
|
Invalid certification data |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li108:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_INVALID_CERTIFICATION_DATA |
« channel[« channel name« ] invalid certification data » |
eNOR |
|
Unknown User |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li109:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_UNKNOWN_USER |
« channel[« channel name« ] unknown user » |
eNOR |
|
Max session key status request exceed |
— |
10 |
4 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li110:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_MAX_SESSION_KEY_STATUS_REQ_EXCEED |
« channel[« channel name« ] max session key status request exceed » |
eNOR |
|
Session key change success |
— |
10 |
6 |
« DNP3_Master » or « DNP3_Outstation » |
remote ip address |
Li111:MNT_ENG_MSG_TYPE_SESSION_KEY_CHANGE_SUCCESS |
« channel[« channel name« ] session key change success » |
eNOR |
HOSTNAME = Local IP address or null.
APPNAME = Commercial reference name, for example, BMEP584040.
PROCID is not used.
MSG:IssuerAdress = Local IP Address.
MSG:Peer is not used.
Event Log Message Descriptions M580 CPUs (firmware V4.0 and later), BMECRA31310, and BMENOR2200H (firmware V3.01 and later)
This topic presents event log message descriptions for:
M580 CPUs with firmware version 4.0 and later (abbreviated “CPU” in column Devices), and
BMECRA31310 adapters (abbreviated “CRA” in column Devices)
BMENOR2200H RTU modules with firmware version 3.01 and later (abbreviated “eNOR” in column Devices)
Event Log Message Descriptions M580 CPUs (firmware V4.0 and later), BMECRA31310, and BMENOR2200H (firmware V3.01 and later)
| Event Title | Event Description | Event additional Description | Severity | PROCID | MSGID | STRUCTURED-DATA | MSG | Devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Successful connection |
All successful connection from a user (human or a component) to a component whether through an encrypted protocol or through an unencrypted protocol if allowed by the customer security policy |
Successful login (Web Server via HTTPS) |
6 |
« HTTPS » |
« CONNECTION_SUCCESS » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Logon » |
CPU, eNOR |
|
Successful login (Firmware upgrade via HTTPS) |
6 |
« HTTPS » |
« CONNECTION_SUCCESS » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Logon » |
CPU CRA, eNOR |
||
|
Successful login (OPC-UA) |
6 |
« OPC-UA » |
« CONNECTION_SUCCESS » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket connection » |
CPU |
||
|
Successful login (Unity Application password via Modbus-Umas)Mode standard only |
6 |
« MODBUS-UMAS » |
« CONNECTION_SUCCESS » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Logon » |
CPU |
||
|
Successful Modbus TCP connection (no user) |
6 |
« MODBUS » |
« CONNECTION_SUCCESS » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket connection » |
CPU CRA, eNOR |
||
|
Successful HTTP/DPWS connection |
6 |
« HTTP » |
« CONNECTION_SUCCESS » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket connection » |
CPU |
||
|
Successful EIP Explicit TCP connection (no user) |
6 |
« EIP » |
« CONNECTION_SUCCESS » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket connection » |
CPU CRA |
||
|
Successful DNP3 connection (no user) |
6 |
« DNP3 » |
« CONNECTION_SUCCESS » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterface peer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket connection » |
eNOR |
||
|
Successful IEC 60870 connection (no user) |
6 |
« IEC60870 » |
« CONNECTION_SUCCESS » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterface peer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket connection » |
eNOR |
||
|
Connection Problem |
All unsuccesful connections from a user (human or a component) to a component whether through an encrypted protocol or through an unencrypted protocol if allowed by the customer security policy |
Login problem (Unity Application password via Modbus-Umas) |
5 |
« MODBUS-UMAS » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Invalid password » |
CPU |
|
Modbus TCP connection problem (no user) |
5 |
« MODBUS » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Max connections reached » « Filtered data flow » |
CPU CRA, eNOR |
||
|
EIP Explicit TCP connection problem (no user) |
5 |
« EIP » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Max connections reached » « Filtered data flow » |
CPU CRA |
||
|
DNP3 connection problem (no user) |
5 |
« DNP3 » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterface peer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Max connections reached » |
eNOR |
||
|
IEC60870 connection problem (no user) |
5 |
« IEC60870 » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterface peer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Max connections reached » |
eNOR |
||
|
Human user account locking due to too many problems during the authentication attempts |
The security policy may request to block a human user account after a configurable number of attempts. This event informs administrator about potential attack & that the human user account must be unlocked. |
Login problem (Web Server via HTTPS). Human user account locking due to too many problems during the authentication attempts |
1 |
« HTTPS » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE_AND_BLOCK » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Invalid certificate » « Invalid password » |
CPU, eNOR |
|
Login problem (firmware upgrade via HTTPS). Human user account locking due to too many unsuccessful authentication attempts |
1 |
« HTTPS » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE_AND_BLOCK » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Invalid certificate » « Invalid password » |
CPU CRA, eNOR |
||
|
Login problem (OPC-UA). Human user account locking due to too many problems during the authentication attempts |
1 |
« OPC-UA » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE_AND_BLOCK » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Invalid certificate » » Invalid password » |
— |
||
|
Denied login (account is blocked) |
A human user tries to connect on an account already blocked. |
Login problem (Web Server via HTTPS). Denied login (account is blocked) |
1 |
« HTTPS » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE_ON_BLOCKED » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« » |
CPU, eNOR |
|
Login problem (firmware upgrade via HTTPS). Denied login (account is blocked) |
1 |
« HTTPS » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE_ON_BLOCKED » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« » |
CPU CRA |
||
|
Login problem (OPC-UA). Denied login (account is blocked) |
1 |
« OPC-UA » |
« CONNECTION_FAILURE_ON_BLOCKED » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« » |
— |
||
|
Disconnection |
A human or a component disconnect manually of after a timeout due to inactivity. |
HTTPS disconnection (Web Server) |
6 |
« HTTPS » |
« DISCONNECTION » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Manual logout » |
CPU, eNOR |
|
HTTPS disconnection (Firmware Upgrade) |
6 |
« HTTPS » |
« DISCONNECTION » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Manual logout » |
CPU CRA, eNOR |
||
|
OPC-UA disconnection |
6 |
« OPC-UA » |
« DISCONNECTION » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket disconnection » |
CPU |
||
|
Modbus disconnection |
6 |
« MODBUS » |
« DISCONNECTION » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket disconnection » |
CPU CRA |
||
|
EIP Explicit disconnection |
6 |
« EIP » |
« DISCONNECTION » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket disconnection » |
CPU CRA |
||
|
HTTP disconnection (DPWS) |
6 |
« HTTP » |
« DISCONNECTION » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket disconnection » |
CPU |
||
|
HTTPS Disconnection triggered by a timeout |
6 |
« HTTPS » |
« DISCONNECTION » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Timeout logout » |
CPU CRA, eNOR |
||
|
OPC-UA Disconnection triggered by a timeout |
6 |
« OPC-UA » |
« DISCONNECTION » |
« [meta sequenceId=num][authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterfacepeer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Timeout logout » |
— |
||
|
DNP3 disconnection |
6 |
« DNP3 » |
« DISCONNECTION » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterface peer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket disconnection » |
eNOR |
||
|
IEC 60870 disconnection |
6 |
« IEC60870 » |
« DISCONNECTION » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [authn@3833 itf=localPort | localInterface peer=peerFQDN:peerPort user=username] » |
« Socket disconnection » |
eNOR |
||
|
Major parameter change at Run Time |
Major Parameters run time change that can cause significant impact on the system |
PLC application parameters change: cycle time |
6 |
« Configuration » |
« PARAMETER_SET » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [config@3833 object= »PLC application » value=value] » |
« Scan time » |
CPU |
|
Backup operation |
Backup of part or total of component |
Download of Application from the PLC |
6 |
« Backup » |
« BACKUP » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [backup@3833 object= »PLC application »] » |
« » |
CPU |
|
Export of Cybersecurity Configuration from BME NUA or BME NOR web pages |
6 |
« Backup » |
« BACKUP » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [backup@3833 object= »Cybersecurity configuration »] » |
« » |
eNOR |
||
|
Restore operation |
Restore of part or total of component |
Upload of a configuration inside a Module |
6 |
« Configuration » |
« CONFIGURATION_CHANGE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [config@3833 object= »Module » |
« » |
CRA |
|
Upload of PLC Application/Configuration inside the PLC |
6 |
« Configuration » |
« CONFIGURATION_CHANGE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [config@3833 object=Object Object = « PLC application » or « PLC configuration » |
« » |
CPU |
||
|
Restore of PLC Application inside the PLC |
6 |
« Backup » |
« RESTORE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [backup@3833 object= »PLC application »] » |
« » |
CPU |
||
|
Import of Cybersecurity Configuration from BME NUA or BME NOR web pages |
6 |
« Backup » |
« RESTORE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [backup@3833 object= »Cybersecurity configuration »] » |
« » |
eNOR |
||
|
Firmware update |
A new firmware has been successfully verified and installed. |
Upload of a new firmware in the device PLC, Copro, Web pages |
6 |
« Configuration » |
« FIRMWARE_UPDATE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [config@3833 object=Object value=version] »Object = « Firmware », « Safety copro », « Web pages » |
« » |
CPU CRA, eNOR |
|
Invalid firmware update |
A new firmware was not installed due to an error. |
A new firmware was not installed because of an incompatible version or invalid signature |
1 |
« Configuration » |
« FIRMWARE_INVALID » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [config@3833 object=Object value=version] »Object = « Firmware », « Safety copro », « Web pages » |
« Incompatible version » « Invalid signature » |
CPU CRA, eNOR |
|
Modification of the time of the device |
A human user request to change time and date. |
— |
5 |
« Configuration » |
« TIME_CHANGE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [config@3833 object=« Time » value=datetime] » |
« » |
CPU |
|
Time signal out of tolerance |
The component shall validate time synchronization messages received through time synchronization channels and alarm if the time synchronization message is not within the tolerances of the component internal/local clock (time in the past, far away, …) |
— |
1 |
« Configuration » |
« TIME_UNEXPECTED » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [config@3833 object= »Time » value=datetime] » |
« Time signal out of tolerance » |
— |
|
Hardware change |
Change detected in network topology |
network physical port change: port link up/down |
6 |
« System » |
« HARDWARE_CHANGE » |
[system@3833 object=Object ]Object = « eth » followed by decimal number |
« Port link up » « Port link down » |
CPU CRA |
|
Any topology change detected from RSTP / HSR / PRP |
6 |
« System » |
« HARDWARE_CHANGE » |
[system@3833 object=Object ]Object = « eth » followed by decimal number |
Port enable Port disable Port learning Port forward Port blocking |
CPU CRA |
||
|
Change detected in Hardware |
M580 SD card insertion/extraction |
6 |
« System » |
« HARDWARE_CHANGE » |
[system@3833 object= »SDCard » ] |
« Insertion » « Extraction » |
CPU |
|
|
Operating mode change |
Program Operating Mode change (Run, Stop, Init, halt)Mode Maintenance / SafeRun / Stop SAFE Task |
— |
5 |
« System » |
« OPERATING_MODE_CHANGE » |
[system@3833 object=Object ]Object = « PLC » or « PLC safe task » or « Module » |
« Init » « Run » « Stop » « Halt » « Maintenance mode » « Safe mode » « Hsby primary » « Hsby secondary » « Hsby wait » « Master » « Non master » |
CPU CRA |
|
Invalid configuration(Outside Cybersecurity) |
A new (not cybersecurity) configuration was not installed due to an error. |
Data integrity error (PLC Application, …) |
1 |
« Configuration » |
« CONFIGURATION_INVALID » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [config@3833 object=Object value=version] »Object= »PLC application » or « Module configuration » |
« Invalid format » « Incompatible version » |
— |
|
Reboot |
Hardware reset or automatic reset after firmware upload |
— |
1 |
« System » |
« REBOOT » |
— |
« Firmware update » « Reset button » |
CPU CRA CRA does not implement Reboot event after Reset button. |
|
Product certificate (and/or keys) modification |
Certificate Management:SL1Product Self-Signed certificate creation |
— |
6 |
« Credential » |
« CERTIFICATE_CHANGE » |
« [meta sequenceId=num] [cred@3833 name=CommonName] » |
« Certificate creation » |
CPU CRA |
NOTE: In addition to the structure described above, each message will also contain the following two fields and values:
Facility = 10
HOSTNAME = Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or local IP address
APPNAME = Commercial reference name, for example, BMEP584040
Event Log Message Descriptions for Control Expert
| EventTitle | Event Description | Facility | Severity | MSG 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Application action |
Creation of a new Control Expert Application |
10 |
6 |
create a new project |
|
Opening of an existing Control Expert Application |
10 |
6 |
open an existing project |
|
|
Saving of the currently opened application |
10 |
6 |
save a project |
|
|
Saving of the currently opened application using a different file |
10 |
6 |
save as a project |
|
|
Importing of an application |
10 |
6 |
import a project |
|
|
Application build in offline mode |
10 |
6 |
build offline |
|
|
Application build in on-line mode PAC in Stop |
10 |
6 |
build on-line stop |
|
|
Application build in Offline mode PAC in RUN |
10 |
6 |
build on-line run |
|
|
Start / stop / initialize the PAC |
10 |
6 |
start stop or initialize the PAC |
|
|
Update initial values with current values |
10 |
6 |
Update init values with current values |
|
|
Upload of the application from the PAC |
10 |
6 |
transfer project from PAC |
|
|
Download of the application to the PAC |
10 |
6 |
transfer project to PAC |
|
|
transfer data values from file to PAC |
10 |
6 |
transfer data values from file to PAC |
|
|
restore project backup in PAC |
10 |
6 |
restore project backup in PAC |
|
|
to project backup in PAC |
10 |
6 |
save to project backup in PAC |
|
|
Change PAC address connection |
10 |
6 |
Set address |
|
|
Control Expert options modifications |
10 |
6 |
Modify options |
|
|
Variable value modification inside the PAC |
10 |
6 |
Modify variable values |
|
|
Variable forcing value modification inside the PAC: internal bits |
10 |
6 |
Force internal bits |
|
|
Variable forcing value modification inside the PAC: outputs |
10 |
6 |
Force outputs |
|
|
Variable forcing value modification inside the PAC: inputs |
10 |
6 |
Force inputs |
|
|
Task management |
10 |
6 |
Task management |
|
|
Task cycle time modification |
10 |
6 |
Task cycle time modification |
|
|
Suppress message in diag viewer |
10 |
6 |
Suppress message in diag viewer |
|
|
Debug executable |
10 |
6 |
Debug executable |
|
|
Replace project variable |
10 |
6 |
Replace project variable |
|
|
Create libraries or families inside the library |
10 |
6 |
Create libraries or families |
|
|
Delete libraries or families inside the library |
10 |
6 |
Delete libraries or families |
|
|
Copy element (DFB/DDT) from the application into the library |
10 |
6 |
Put object into library |
|
|
Delete element (DFB/DDT) into the library |
10 |
6 |
Delete object from library |
|
|
Copy element (DFB/DDT/EF/EFB) from the library into the application |
10 |
6 |
Get object from library |
|
|
Modify documentation (application printing) |
10 |
6 |
Modify documentation |
|
|
Modify functional view |
10 |
6 |
Modify functional view |
|
|
Modify animation tables |
10 |
6 |
Modify animation tables |
|
|
Modify constant values |
10 |
6 |
Modify constant values |
|
|
Modify program structure |
10 |
6 |
Modify program structure |
|
|
Modify program sections |
10 |
6 |
Modify program sections |
|
|
Modify Project settings |
10 |
6 |
Modify Project settings |
|
|
Variable created / removed into Data editor |
10 |
6 |
Variable Add Remove |
|
|
Variable attribute modified |
10 |
6 |
Variable Main Attributes modification |
|
|
Variable attribute modified |
10 |
6 |
Variable Minor Attributes modification |
|
|
DDT Created / Removed into Data Editor |
10 |
6 |
DDT Add Remove |
|
|
DDT Modified into Data Editor |
10 |
6 |
DDT modification |
|
|
DFB Created / Removed into Data Editor |
10 |
6 |
DFB type Add Remove |
|
|
DFB structure modified into Data Editor |
10 |
6 |
DFB type structure modification |
|
|
DFB sections modified |
10 |
6 |
DFB type sections modification |
|
|
DFB instance Modification into data editor |
10 |
6 |
DFB instance Modification |
|
|
DFB instance Minor Attributes modification into Data Editor |
10 |
6 |
DFB instance Minor Attributes modification |
|
|
PAC Configuration modification |
10 |
6 |
Modify configuration |
|
|
PAC I/O Sniffing |
10 |
6 |
IO sniffing |
|
|
PAC I/O Configuration modification |
10 |
6 |
Modify the IO configuration |
|
|
PAC I/O Configuration adjust |
10 |
6 |
Adjust the IO |
|
|
PAC I/O Configuration Save Param from I/O Screen |
10 |
6 |
Save param |
|
|
PAC I/O Configuration Save Param from I/O Screen |
10 |
6 |
Restore param |
|
|
Operator Screens modification |
10 |
6 |
Modify screens |
|
|
Modify messages |
10 |
6 |
Modify messages |
|
|
Operator Screens : Family / Screen added / removed |
10 |
6 |
Add/Remove screens or families |
|
|
Move FFB block |
13 |
6 |
Move component |
|
|
Move Contact/Coil |
13 |
6 |
Move component |
|
|
Insert FFB Block |
13 |
6 |
Insert component |
|
|
Insert Contact/Coil |
13 |
6 |
Insert component |
|
|
Delete FFB Block |
13 |
6 |
Delete component |
|
|
Delete Contact/Coil |
13 |
6 |
Delete component |
|
|
Set Effective parameter on FFB Block |
13 |
6 |
Add variable |
|
|
Set Effective parameter on Contact/Coil |
13 |
6 |
Add variable |
|
|
Remove Effective parameter on FFB Block |
13 |
6 |
Delete variable |
|
|
Remove Effective parameter on Contact/Coil |
13 |
6 |
Delete variable |
|
|
Change Effective parameter on FFB Block |
13 |
6 |
Modify variable |
|
|
Change Effective parameter on Contact/Coil |
13 |
6 |
Modify variable |
|
|
Make a link between two pins |
13 |
6 |
Link pin |
|
|
Change size of extensible FFB block |
13 |
6 |
Scale component |
|
|
Change size of vertical/horizontal link |
13 |
6 |
Scale component |
|
|
Rename effective parameter |
13 |
6 |
Rename variable |
|
|
Delete one single row |
13 |
6 |
Delete row |
|
|
Delete multiple rows |
13 |
6 |
Delete rows from |
|
|
Delete one single column |
13 |
6 |
Delete column |
|
|
Delete multiple columns |
13 |
6 |
Delete columns from |
|
|
Insert one single row |
13 |
6 |
Insert row |
|
|
Insert multiple rows |
13 |
6 |
Insert rows from |
|
|
Insert one single column |
13 |
6 |
Insert column |
|
|
Insert multiple columns |
13 |
6 |
Insert columns from |
|
|
DTM action |
DTM Download parameter finished in error |
9 |
6 |
Download parameters to device service finished in error |
|
DTM Download parameter finished without error |
9 |
6 |
Download parameters to device service finished without error |
|
|
DTM Upload parameter finished in error |
9 |
6 |
Upload parameters from device service finished in error |
|
|
DTM Upload parameter finished without error |
9 |
6 |
Upload parameters from device service finished without error |
|
|
Connection to the DTM is not established |
9 |
6 |
Go on-line service failed |
|
|
Connection to the DTM succeeded |
9 |
6 |
Go on-line service succeeded |
|
|
Connection to the DTM is not closed |
9 |
6 |
Go offline service failed |
|
|
Connection to the DTM closed successfully |
9 |
6 |
Go offline service succeeded |
|
|
DTM FDR download parameters service is not performed |
9 |
6 |
FDR download parameters service failed |
|
|
DTM FDR download parameters service succeeded |
9 |
6 |
FDR download parameters service succeeded |
|
|
DTM FDR upload parameters service is not performed |
9 |
6 |
FDR upload parameters service failed |
|
|
DTM FDR upload parameters service succeeded |
9 |
6 |
FDR upload parameters service succeeded |
|
|
Download parameters to device service is not performed |
9 |
6 |
Download parameters to device service failed |
|
|
Download parameters to device service succeeded |
9 |
6 |
Download parameters to device service succeeded |
|
|
Upload parameters from device service is not performed |
9 |
6 |
Upload parameters from device service failed |
|
|
Upload parameters from device service succeeded |
9 |
6 |
Upload parameters from device service succeeded |
|
|
Audit Trail Function Event |
9 |
6 |
Audit Trail Function Event |
|
|
Audit Trail Device Status Event |
9 |
6 |
Audit Trail Device Status Event |
|
|
No device status message |
9 |
6 |
No device status message |
|
|
Status information |
9 |
6 |
Status information |
|
|
Access right : Read / Write |
9 |
6 |
Access right : Read / Write |
|
|
Enumerator entry |
9 |
6 |
Enumerator entry |
|
|
Password action |
Problem at application PSW changing |
2 |
6 |
CyberSecurity – Modifying Password > Incorrect Password |
|
Problem at application PSW verification |
2 |
6 |
CyberSecurity – Verifying Password > Incorrect Password |
|
|
Problem at section PSW verification |
2 |
6 |
CyberSecurity – Verifying Section Password > Incorrect Password |
|
|
PSW « DataStorage » changed |
2 |
6 |
CyberSecurity – Data Storage Password Modified |
|
|
PSW « FW Download » changed |
2 |
6 |
CyberSecurity – Firmware Password Modified |
|
|
Problem at application PSW verification |
2 |
6 |
CyberSecurity – Verifying Password > Incorrect Password |
|
|
SYSLOG configuration changed |
CyberSecurity – Event Logging project setting has changed – Event Logging, SYSLOG server address, port or protocol |
– |
– |
SYSLOG address changed |
|
File action |
File XXXXX open |
0 |
6 |
XXXXX file has been opened |
|
PAC disconnected = @XXXXXX driver = YYYYYY |
0 |
6 |
Disconnection from PAC @=XXXXXX dirver= YYYYY |
|
|
Application XXXXXX close |
0 |
6 |
Close application XXXXXX |
|
|
Transfer from PAC to PC |
0 |
6 |
project has been transfered from PAC to PC |
|
|
1. MSG content includes the concatenation of the Username, the PID of Control Expert, plus the message. |
||||
| Refid[27] | Clock Source |
|---|---|
| GOES | Geosynchronous Orbit Environment Satellite |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| GAL | Galileo Positioning System |
| PPS | Generic pulse-per-second |
| IRIG | Inter-Range Instrumentation Group |
| WWVB | LF Radio WWVB Fort Collins, Colorado 60 kHz |
| DCF | LF Radio DCF77 Mainflingen, DE 77.5 kHz |
| HBG | LF Radio HBG Prangins, HB 75 kHz (ceased operation) |
| MSF | LF Radio MSF Anthorn, UK 60 kHz |
| JJY | LF Radio JJY Fukushima, JP 40 kHz, Saga, JP 60 kHz |
| LORC | MF Radio Loran-C station, 100 |
| TDF | MF Radio Allouis, FR 162 kHz |
| CHU | HF Radio CHU Ottawa, Ontario |
| WWV | HF Radio WWV Fort Collins, Colorado |
| WWVH | HF Radio WWVH Kauai, Hawaii |
| NIST | NIST telephone modem |
| ACTS | NIST telephone modem |
| USNO | USNO telephone modem |
| PTB | German PTB time standard telephone modem |
| MRS | Multi Reference Sources |
| XFAC | Inter Face Association Changed (IP address changed or lost) |
| STEP | Step time change, the offset is less than the panic threshold (1000 s) but greater than the step threshold (125 ms) |
| GOOG | Unofficial Google Refid used by google NTP servers as time4.google.com |
Source de l’information
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_Time_Protocol
50 feuilles de lierre lavé et ciselées (environ 50g sans les queues)
1 litre d’eau
faire bouillir 15mn
laisser macérer à couvert 12h
filtrer
Mettre les bouteilles dans le frigo
Ajouter bicarbonate ou percarbonate pour blanchir (1 c à soupe)
Parfumer plus ou moins si nécessaire
Utiliser un pot à yaourt par machine
—————————-
ou faire bouillir 10mn en remuant et laisser macérer 24h
——————————
ou 100g de lierre grimpant ciselée lavées équeutées
laisser bouillir 10 mn
laisser macérer 24h
——————————-
ou 75g de feuilles
1.2 l d’eau
20g savon de marseille en paillettes à ajouter le lendemain et refaire bouillir
Mettre un verre de mélange par machine
Recette fournie par Francis C.
Nom : pool.ntp.org
Addresses: 37.187.104.44
62.210.244.146
194.57.169.1
51.15.191.239
Nom : time.google.com
Addresses: 2001:4860:4806::
2001:4860:4806:4::
2001:4860:4806:c::
2001:4860:4806:8::
216.239.35.4
216.239.35.8
216.239.35.12
216.239.35.0
Nom : ntp1.glb.nist.gov
Addresses: 2610:20:6f97:97::4
132.163.97.3
Aliases: time.nist.gov